
Customer-Facing Analytics
What Is Customer-Facing Analytics?
Customer-facing analytics gives your customers access to data, dashboards, and reports inside your product. It places insight into the same interface where they already work, eliminating the need for an external BI tool.
These analytics run on top of embedded analytics and support use cases that require interactive dashboards, self-service analytics, and data visualization built into the application. Many teams call this user-facing analytics or client-facing analytics, but the goal is the same. You give customers a fast way to explore their own data without leaving the product
Some products also support embedded reporting for formatted outputs.
Most customer-facing analytics rely on an analytics SDK and direct embedding instead of iFrame embedding. This keeps the experience fully branded and allows support for features like role-based access, data refresh, and row-level security. It also gives you the control you need to provide reliable, scalable analytics inside a multi-tenant environment.
Customer-Facing Analytics vs Traditional BI
Many companies still rely on enterprise BI software designed for internal reporting. That approach breaks when you bring analytics into a customer-facing product. Traditional BI tools sit outside the application and push users into separate portals, which disrupts the product experience and slows their decisions. This gap becomes even clearer when compared with modern embedded analytics.
Customer-facing analytics takes a different path. It embeds data visualization, embedded dashboards, and interactive analysis inside the product through an analytics SDK. Users work with live data in context without switching tools or losing focus. This improves adoption because customers see analytics as part of the product, not an external system.
Traditional BI also depends on complex workflows. It requires IT, manual report building, and heavy maintenance. It was never built for multi-tenant analytics, row-level security at scale, or white-label analytics that match your product’s UI. These limits show quickly when you try to support customer workflows.
Customer-facing analytics works within modern development frameworks through direct embedding rather than iFrame embedding. It avoids all iFrame embedding challenges and supports API-driven analytics, role-based access, data refresh, and predictable performance. This lets you deliver a secure and consistent experience inside a cloud product.
For a deeper comparison, see embedded analytics vs traditional BI.
This shift changes how companies think about BI. Analytics becomes part of the product, not an external destination. The next step is understanding how these capabilities support product growth and customer value.
Customer-Facing Analytics Features
Many teams still ask what customer-facing analytics is expected to deliver inside a modern SaaS product. Strong features matter because they shape the user experience and reduce the workload on your developers. Good customer-facing analytics gives customers fast insight while keeping your product lightweight and scalable.
Direct Integration
Customer-facing embedded analytics works best when it integrates directly with your codebase. The solution should offer an analytics SDK, API-driven workflows, and full white-label control. Avoid iFrame embedding because it limits UI control and slows the experience, as described in the embedded analytics vs iFrames article. Direct integration keeps analytics native to your product.
Visualization Components
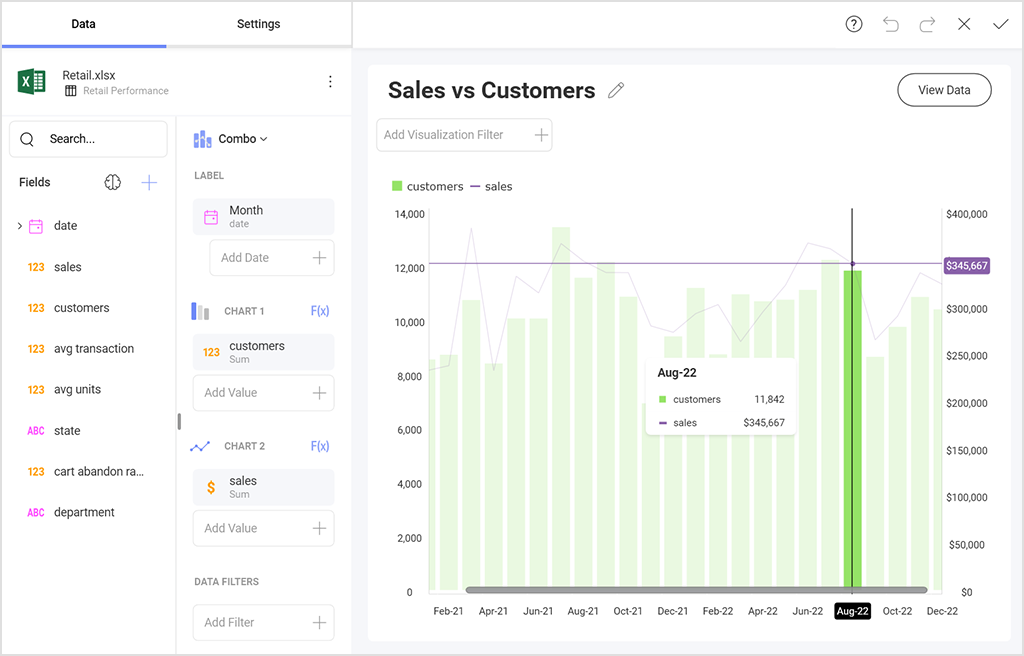
Customers need clear visuals to understand their data. Embedded dashboards should support interactive charts, exploratory analysis, guided insights, and data storytelling. A flexible visualization library also reduces engineering effort and supports advanced UI work. Teams that need deeper control can also create custom data visualizations.
Self-Service Analytics
A core part of what customer-facing analytics includes is letting customers explore their own data. They should filter, edit, and build dashboards without relying on your team. This reduces support requests and helps developers stay focused on core work. Many teams evaluate self-service needs through ideas similar to self-service BI.
Data Connectivity and Performance
Reliable data access is essential for customer-facing embedded analytics. The solution must support live data, predictable data refresh, and stable links to your data sources. Query performance optimization keeps dashboards fast as your product grows. This is the cornerstone behind scalable analytics.
Security and Governance
Strong customer-facing analytics supports row-level security, multi-tenant controls, SSO, and audit logs. These features protect customer data and give you a clean way to enforce rules through code rather than manual processes.
Advanced Insights
Predictive analytics, automated insights, and conversational analytics help customers understand complex information. These features increase adoption and add value without requiring more dashboards or custom reports. Modern products often extend these capabilities with AI-powered analytics and insights.
Build vs Buy Customer-Facing Analytics
Adding analytics to a product forces teams to decide how much they want to build and how much they want to own. This choice affects engineering workload, delivery timelines, and how quickly customers get the insight they expect. Strong customer-facing analytics demands features that take time to design, test, and maintain, so the build vs buy question comes up early for most SaaS teams.
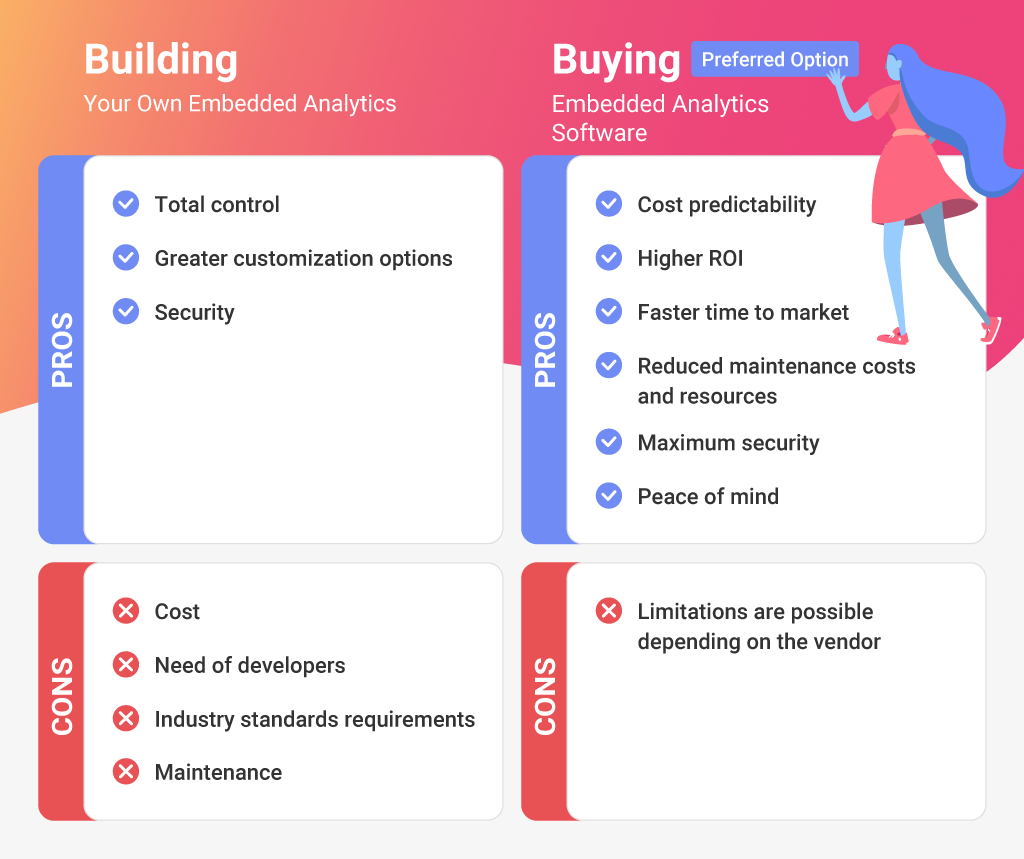
Building gives full control. It also requires a serious investment in architecture. Your team must create embedded dashboards, design visualization components, support self-service editing, and manage data refresh. You also own multi-tenant analytics, row-level security, SSO, audit logs, and every part of the governance model. This work continues long after the first release and brings several embedded analytics integration challenges.
Buying simplifies the effort. Customer-facing embedded analytics provides an analytics SDK, a visualization library, and direct integration embedding. These tools help you deliver interactive dashboards, exploratory analysis, and predictive or automated insights without building them from scratch. This keeps development focused on the core product and helps teams reduce time-to-market.
A strong customer-facing embedded analytics platform also handles stability and security. It supports RLS, live data, and API-driven analytics. It connects cleanly to your data pipeline and scales with your customer base. Many teams evaluate this through the ROI of embedded analytics.
These trade-offs shape how customer-facing analytics fits into a modern SaaS roadmap and define the point at which embedded capabilities deliver more value than custom development.
The Benefits of Customer-Facing Analytics
Customer-facing analytics improves how customers understand and use your product. It also reduces the work required from your team. These benefits shape how well the product supports long-term growth.
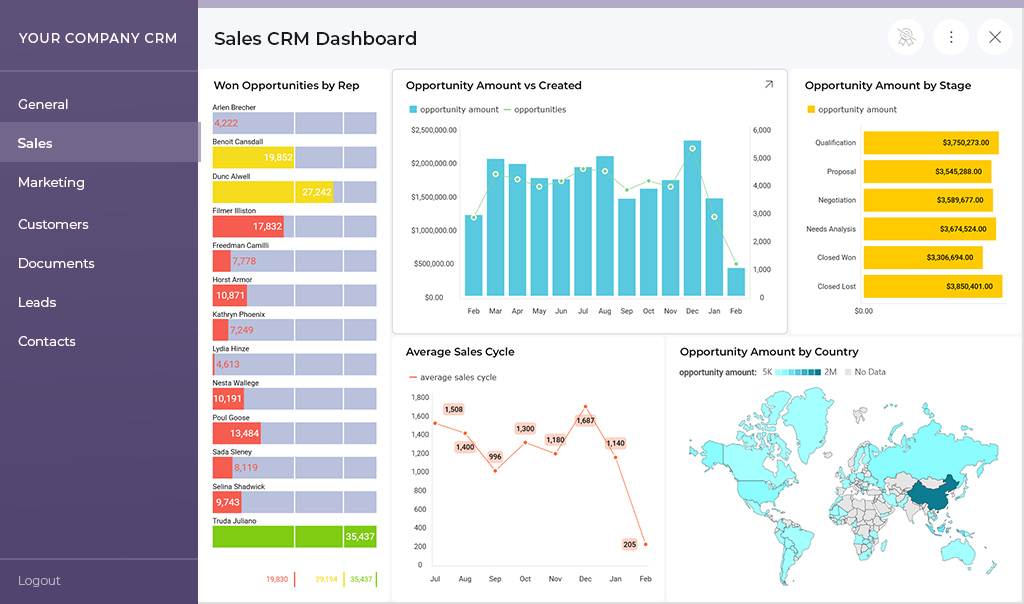
• Higher product adoption: Embedded dashboards appear where customers already work, so they use them more often. Adoption patterns often correlate with product analytics and user behavior trends.
• Better customer retention: When customers see their own trends and results, they understand the value your product provides. Embedded analytics statistics also show strong adoption and retention links.
• Fewer support requests: Self-service analytics reduces dashboard requests and one-off report work. Customers explore data on their own, and developers stay focused on core tasks.
• Faster onboarding: Clear data visualization helps new users learn the product quickly.
• New monetization paths: Teams often package advanced dashboards, predictive models, or guided insights as premium features. Many explore new revenue models using analytics revenue impact strategies.
• Lower long-term development cost: Customer-facing embedded analytics provides an analytics SDK, direct integration, and stable data refresh. This keeps maintenance predictable and aligns with scalable analytics.
• Better product differentiation: Strong analytics improves the overall product experience. It helps teams stand out in markets where most tools still rely on external BI systems.
These benefits help products grow faster and give customers a clearer experience inside the application.
Security in Customer-Facing Analytics
Security defines how customer-facing analytics fits inside a SaaS product. Customers expect insight, but they also expect strong data protection at every layer of the system. Effective solutions follow the principles of embedded analytics security.
Row-level security (RLS)
RLS ensures each customer sees only their own data. It applies filters at the query or API level and protects multi-tenant analytics environments.
Multi-tenant data isolation
A secure design separates data for each tenant and prevents cross-account access. This is essential for customer-facing embedded analytics in any cloud product.
Single Sign-On (SSO)
Support for SAML, OAuth, or OpenID Connect keeps authentication consistent with the rest of the product. It also removes the need for separate login flows.
Role-based authorization
API-driven permissions define what each user can see or change. This keeps control flexible and reduces manual configuration.
Audit logs
Logs track who viewed dashboards, exported data, or adjusted reports. This helps teams meet compliance needs and monitor system behavior.
Secure data pipelines
A secure data pipeline protects data refresh operations and encrypts information in transit and at rest. It also limits access to sensitive data.
Governance controls
Teams use governance rules to manage access, versioning, and data use. These controls keep analytics consistent as the product expands.
Strong security makes customer-facing analytics reliable. It protects customer data, maintains performance, and supports long-term trust in the product.


